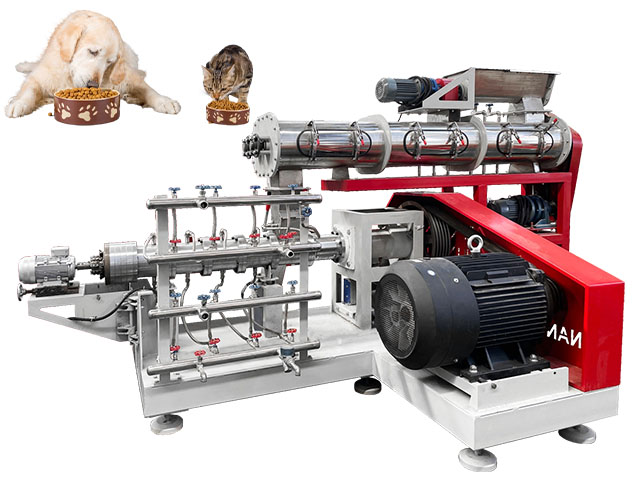
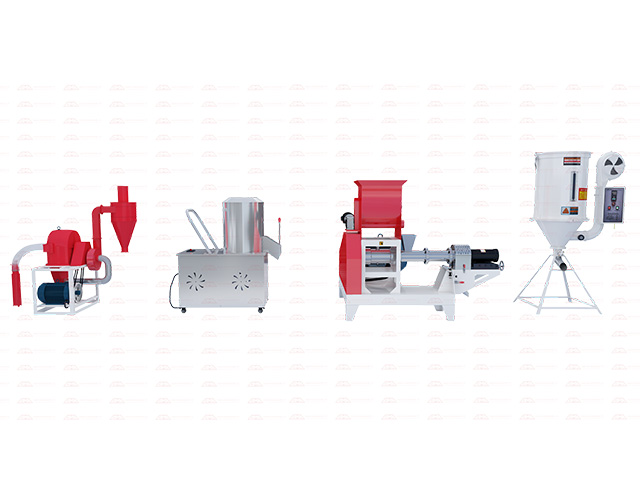
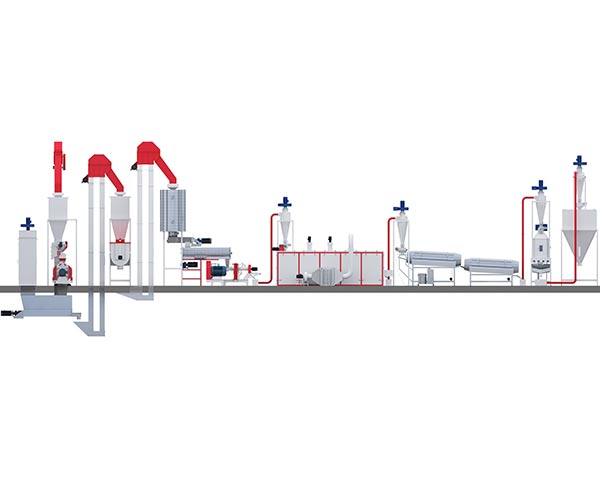
What are the factors that affect the quality of feed pellets?
1. Raw Materials
The type of grain used (corn or wheat) and its percentage will affect the quality, as the target temperature required for gelatinization varies depending on the source of the starch.
| Source of Starch | Gelatinization Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Barley | 51-60 |
| Wheat | 58-64 |
| Rye | 57-70 |
| Oat | 53-59 |
| Corn | 62-72 |
| Sorghum | 68-78 |
| Rice | 68-78 |
Another factor is the addition of fat (more than 1%), regardless of the source (animal or plant), which can greatly impair the quality of the particles.
2. The fineness of the raw materials
The fineness of the raw materials is another factor that affects the final particle quality. Generally speaking, the finer the raw materials are ground, the higher the quality of the granulation.
This is because finer raw material powders can be more fully exposed to surrounding particles, thereby expanding the contact area between granulation powders. Sufficient contact makes the granulation process more efficient, strengthens the bonding between powders, and results in denser particles.
3. Equipment condition


The condition of production equipment also determines the quality of the particles. This point is so crucial that it often does not receive proper attention in the daily operations of feed mills.
Wear and tear on hammers, molds, rollers, and other components, or improper positioning or orientation of blades or steam injection valves, can adversely affect the quality of the particles.
4. Pelletizing process
A well-executed pelletizing process is crucial as it directly determines:
- Durability
- Powder consistency
- Efficiency of the pelletizing process (yield and energy consumption)
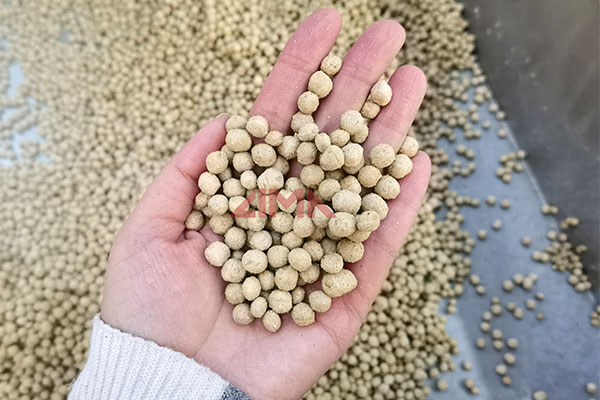

Temperatures above 80-85°C are optimal for starch gelatinization. The steam used must be adjusted after leaving the boiler and before entering the conditioner to ensure sufficient steam quantity and temperature for thorough gelatinization of the material.
Key adjustments focus on steam flow rate and retention time, both critical for the pelletizing process. Additionally, steam can carry essential oils from grains, lubricating the material to reduce mechanical friction and wear, thereby enhancing pelletizer production efficiency (tons per hour).